How It Works
Step 1: Awake State
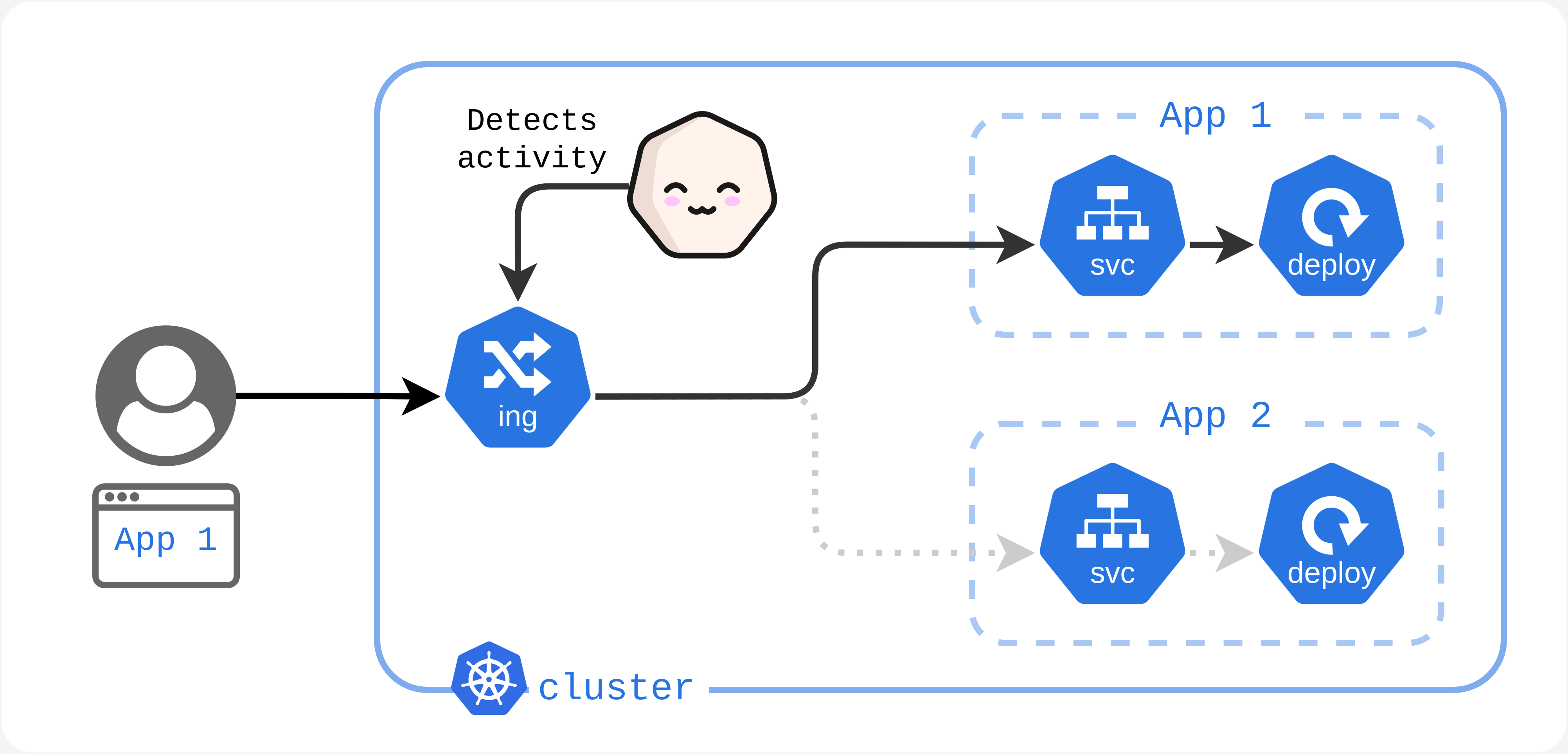
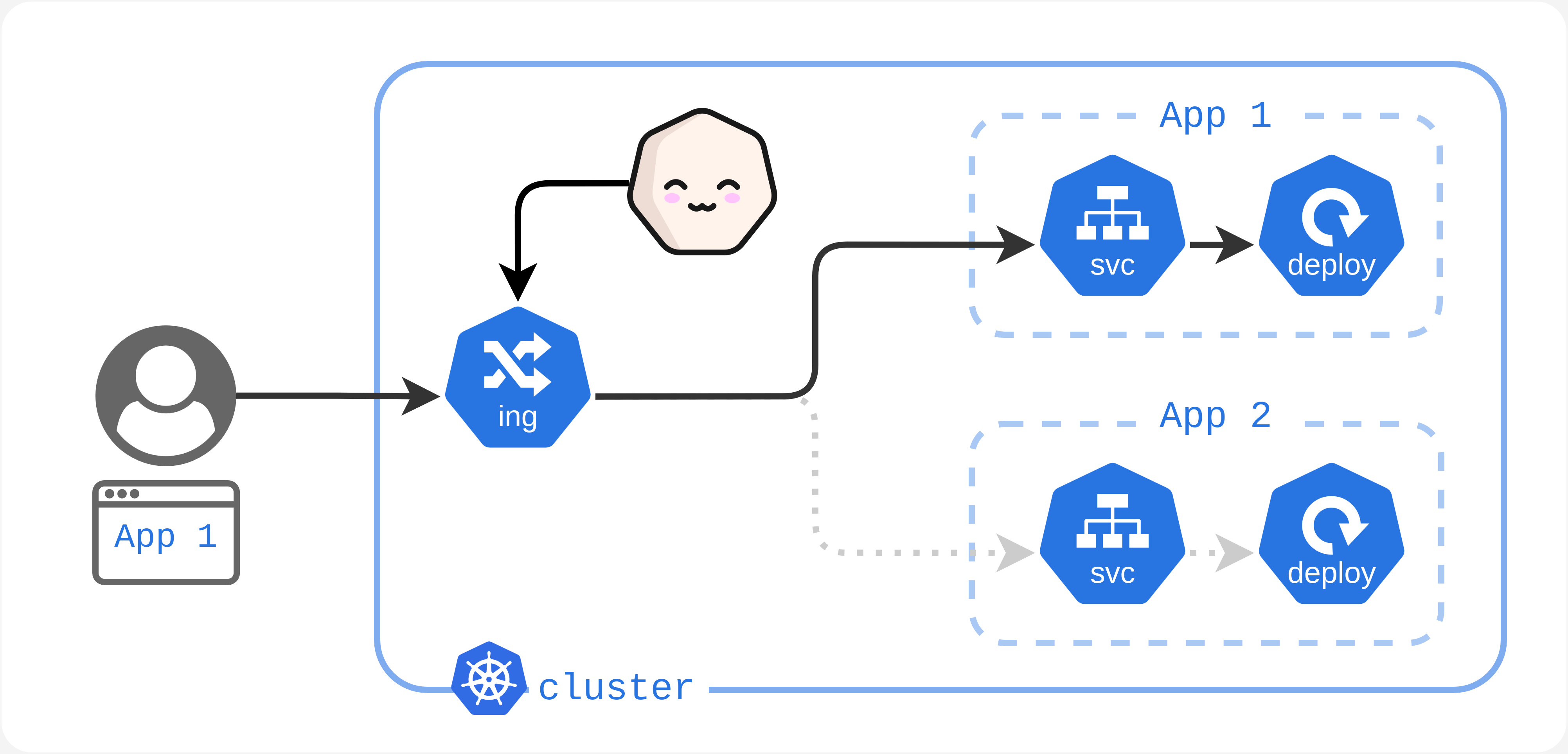
Your cluster receives traffic. Kubesleeper detects this activity.
> Your cluster is in an Awake state.
Step 2: Sleepiness State
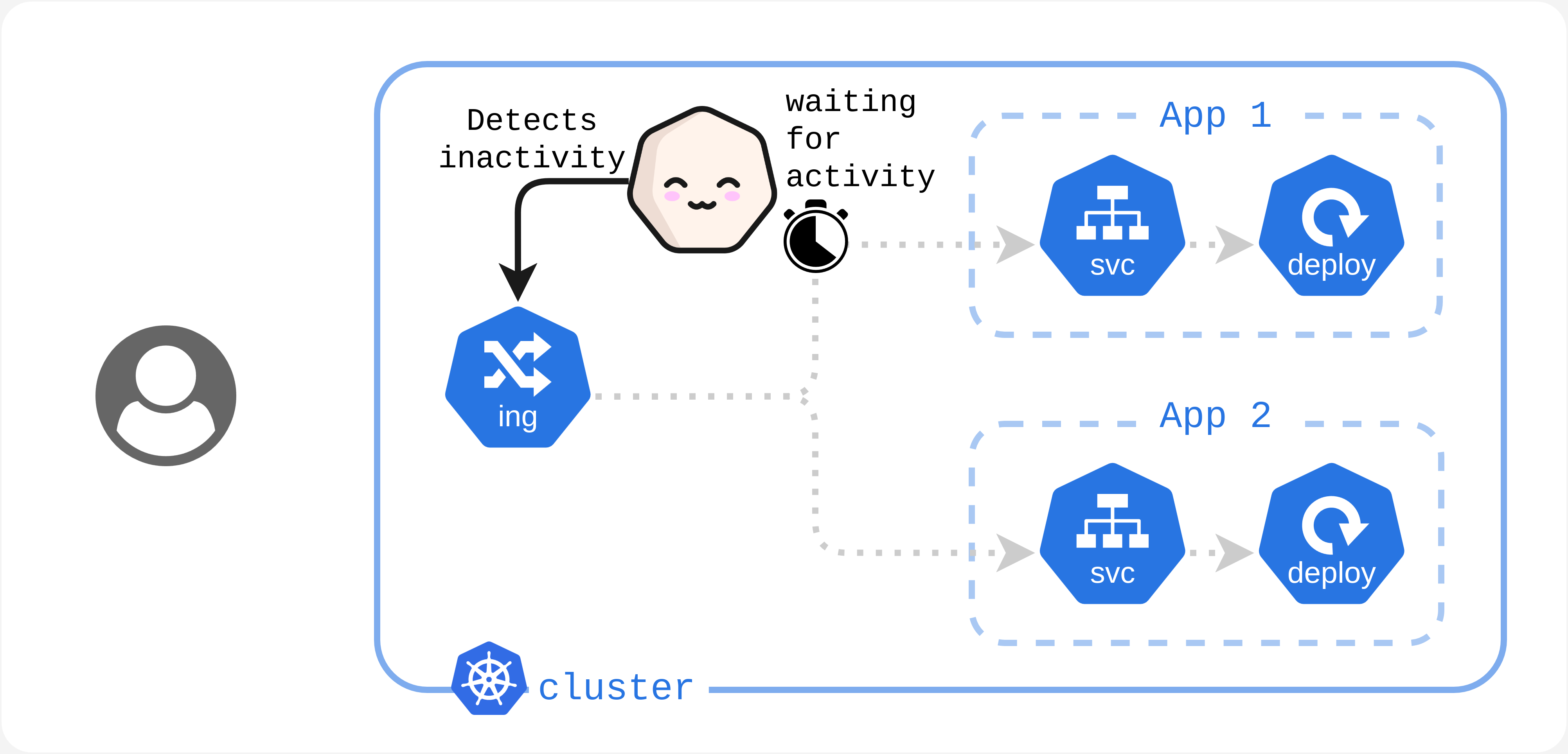
Your cluster stops receiving traffic. Kubesleeper waits a bit to check if the lack of activity is just temporary or if it should transition your cluster to an Asleep state.
> Your cluster is in a Sleepiness state.
Step 3: Asleep State - Scaling Down
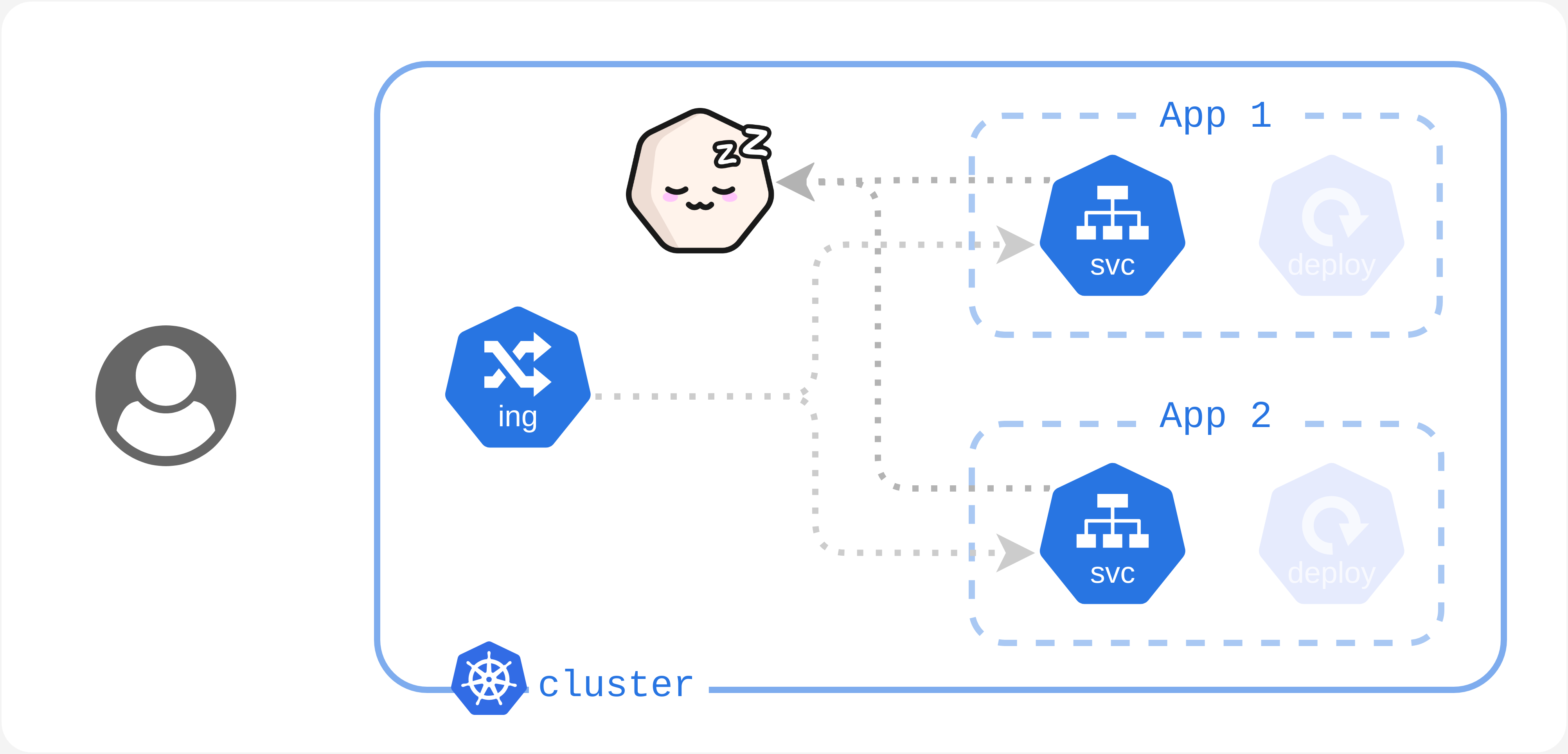
Your cluster has not received any traffic for a certain duration. Kubesleeper will set your cluster off, which means:
- Load resources (Deployments) are turned off (
replicas: 0). - Services redirect traffic to Kubesleeper instead of their normal load resources.
> Your cluster is in an Asleep state.
Step 4: Asleep State - Scaling Up
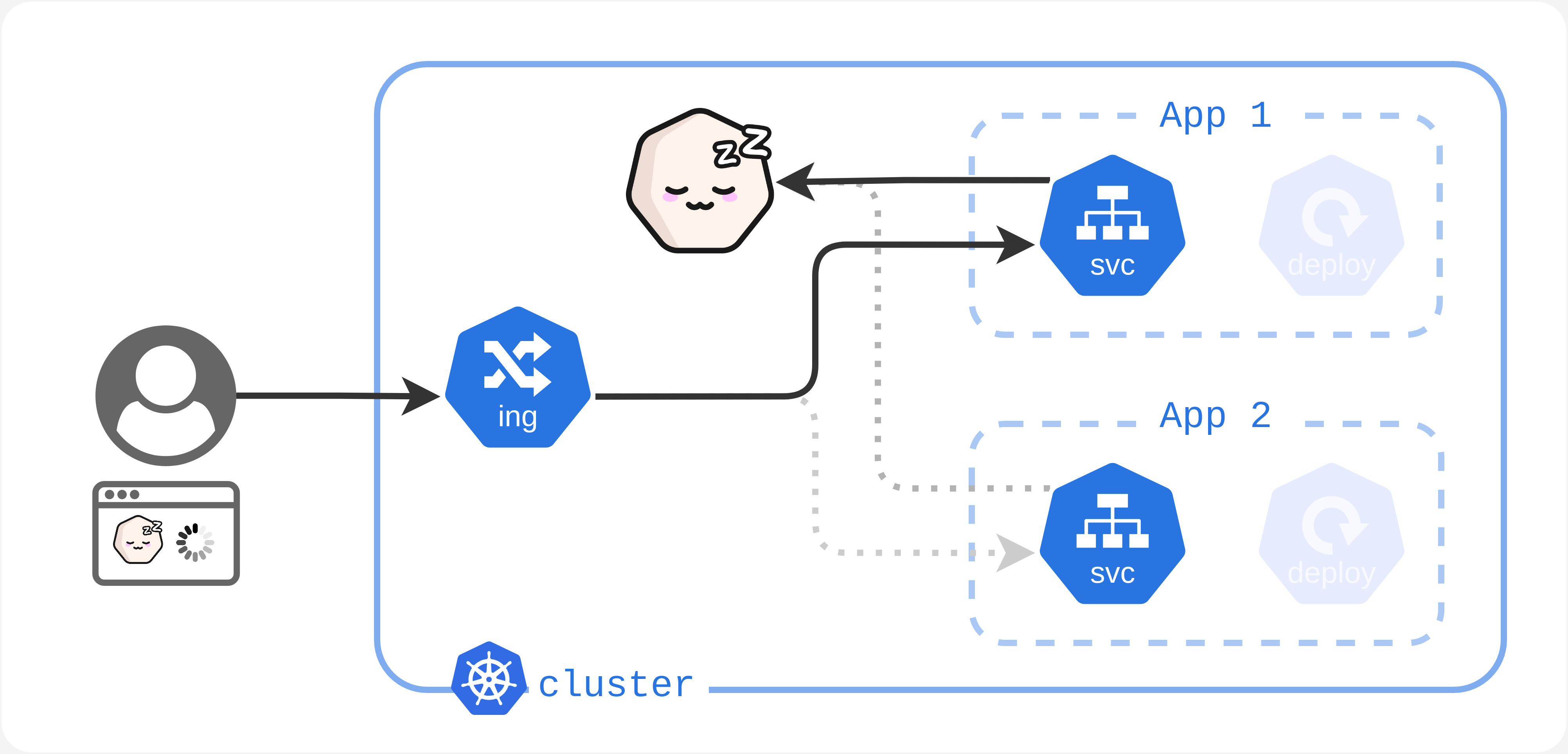
Your cluster receives new traffic. This traffic has been redirected to Kubesleeper because there are no resources currently handling it. Kubesleeper will then turn on all resources. Since it can take a short amount of time (a few seconds) for your pods to become fully operational, Kubesleeper sends a waiting page to the users.
Turning on the cluster means:
- Load resources (Deployments) are turned on (
replicas: {same number as when they were turned off}). - Services redirect the traffic back to their normal load resources.
> Your cluster is in Asleep state (but is waking up).
Step 5: Back to Awake State
Your cluster is in a normal state (like Step 1).
> Your cluster is in an Awake state.